According to the 2020 National Diabetes Statistics Report, obesity has become a global health concern. It reveals concerning trends in obesity and its association with diabetes:
People with obesity have also shown resistance to insulin, which adds to the concerns as it is a precursor to diabetes. This resistance occurs when fat, muscle, and the liver become less responsive to insulin, prompting the pancreas to produce more insulin to meet increased demand.

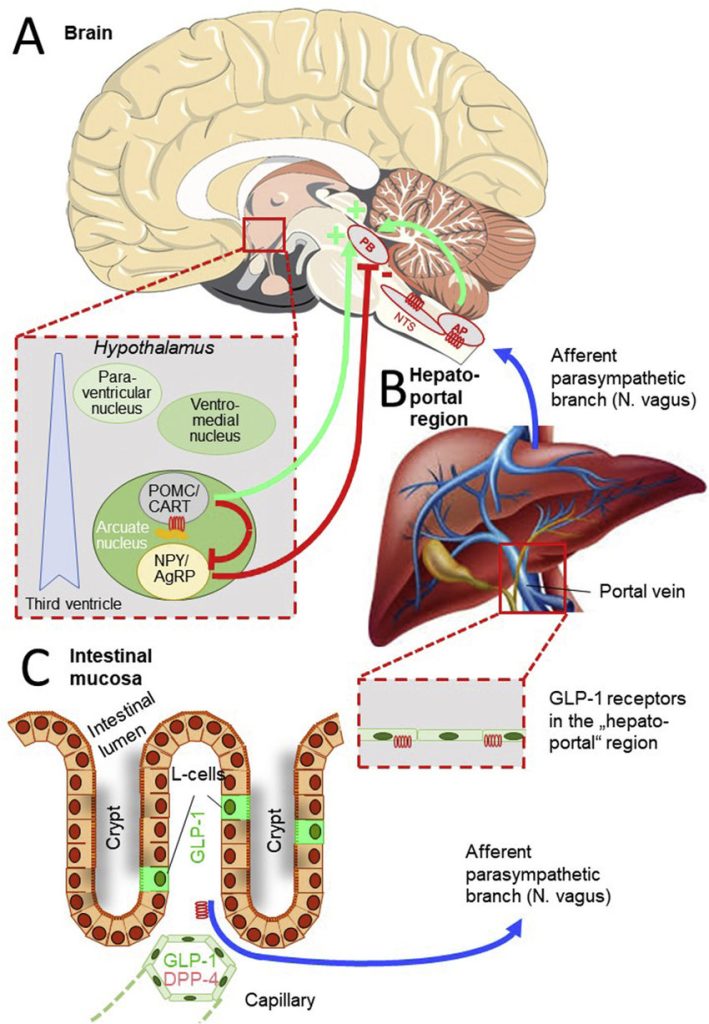
In the central nervous system, GLP-1 receptors are located in the hypothalamus, which is involved in regulating food intake
The reduced feelings of hunger were associated with an increase in functional connectivity of the nucleus tract with the hypothalamus
GLP-1 directly stimulates POMC/CART neurons and indirectly inhibits neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP) to increase measures of satiety and decrease hunger
Monday – Friday: 10am – 4pm
Saturday – Sunday: By appointment

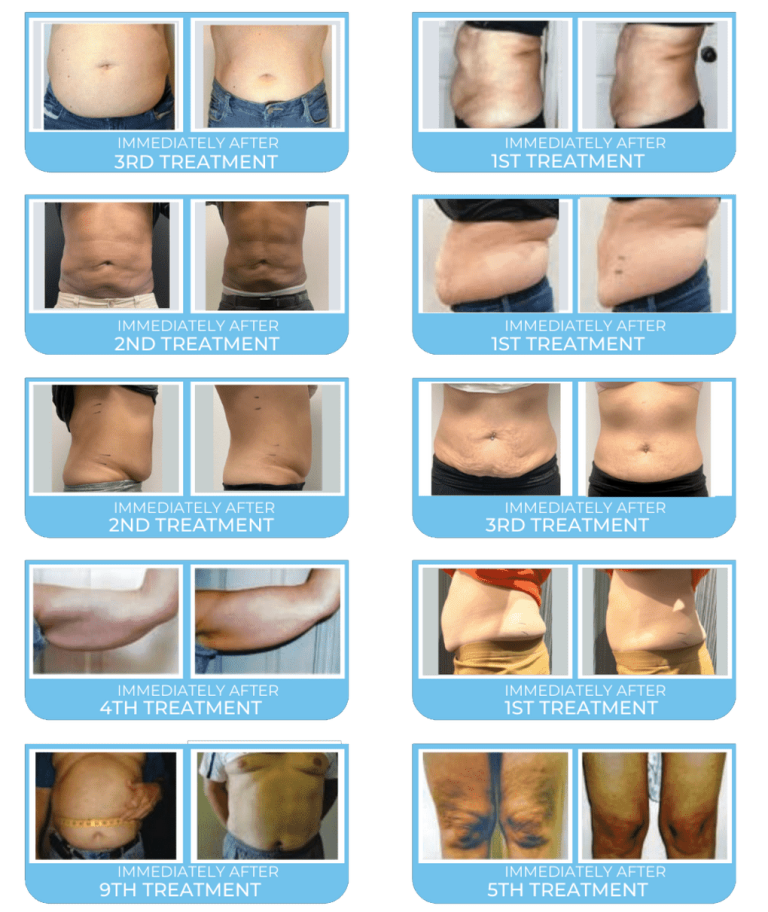
REAL RESULTS, EVERY TREATMENT.